| GEOGRAPHY KEY POINTS |
INDIA – POSITION & EXTEND
LOCATION
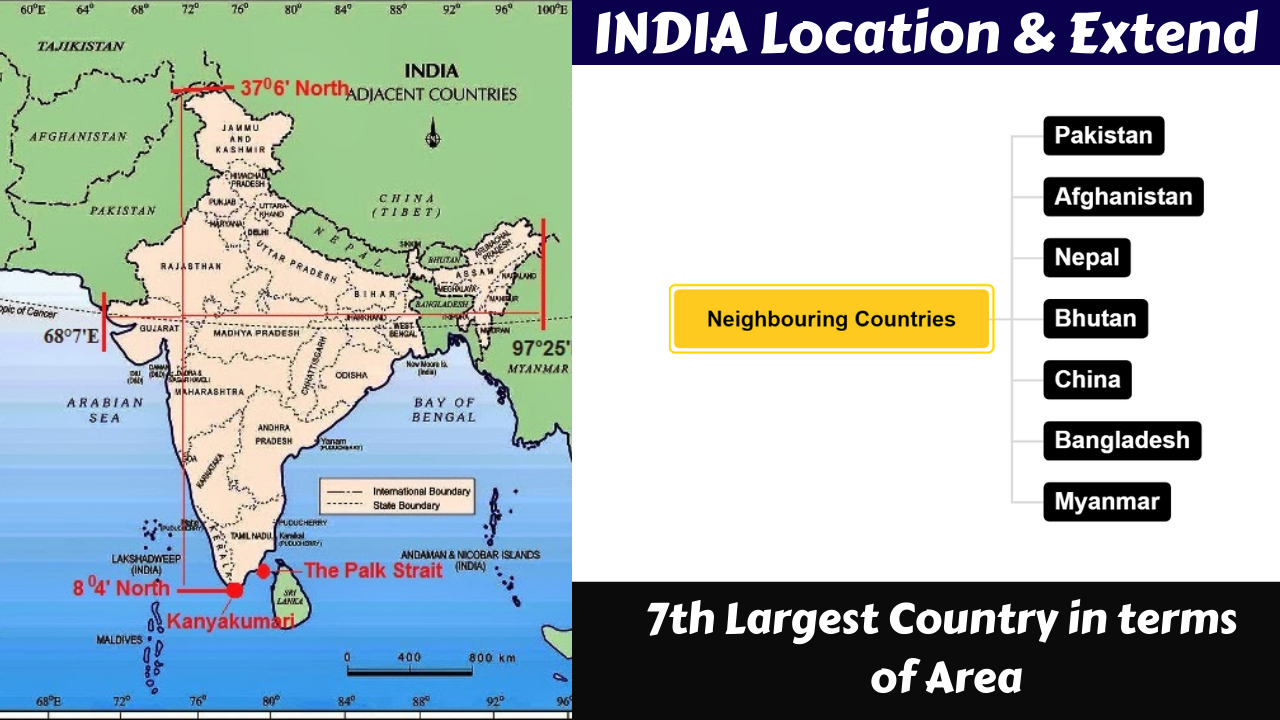
India is located within both Northern Hemisphere and Eastern Hemisphere
India is a peninsula situated in South Asia.
The mainland of India extends from 80.4′ to 370.6′ North latitude and from 680.7′ to 970.25′ East longitude
The Indira Point is the southern most point of India is located in the Nicobar island at 60.45′ N. Latitude
The northern tip of India is Indiracol in Jammu and Kashmir
The Tropic of Cancer (23 1/20N) passes through the middle of the country
82 1/20E longitude is the central meridian of India, Indian Standard Time (IST) is based on it
EXTEND
India is the 7th largest country in the world in terms of area
India has a total area of 32,87, 263 Km2
Area from East to West : 2933 km
Area from North to South : 3214 km
FRONTIER
The land frontiers of the country is about 15,200 km
Natural frontier in the north between India and China : Himalayan ranges
The mainland of India has water frontier of about 6100 km
The total length of India’s coastline is 7516.5 km
The Arabian Sea in the west, the Indian Ocean in the south and the Bay of Bengal in the east form the water frontiers
NEIGHBOURING COUNTRIES
India has 7 neighbouring countries
NORTH WEST : Pakistan and Afghanistan are Located
NORTH : Nepal, Bhutan and China are Located
EAST : Bangladesh and Myanmar are Located
SOUTH EAST : Sri Lanka is Located
BOUNDARY LINES
Between India & Srilanka : Palk Strait and the Gulf of Mannar
Between India and Pakistan : Radcliff line
Between India and Afghanistan : Durand line
Between India and China : Mac Mohan Line
ADMINISTRATIVE DIVISIONS
29 States
7 Union Territories
Largest State (in terms of Area): Rajasthan
Smallest State (in terms of Area) : Goa
| HISTORY KEY POINTS |
ADVENT OF EUROPEANS TO INDIA

After the success of the Portuguese in trade with India, the Dutch, French and the English arrived in India for trade, this changed the history of India and European Countries
PORTUGUESE
They were 1st European Company to arrive in India for Trade and last to leave through sea route
Governor General Francisco De Almeida Implemented Blue water Policy
Alfonso de Albuquerque is considered as real founder of Portuguese Empire in India
In 1510 Alfonso de Albuquerque waged battle against Sultan of Bijapur and Won Goa
Their power declined with arrival of French and British in India
DUTCH
They arrived to India from Holland or Netherlands
In 1602 they established United East India Company
They had warehouses in Surat, braoch, Cambe, Cochin, Nagapatinam, Masulipatnam and Chinsura
There power declined as they were unable to face French and British
They got themselves limited to Spice Islands in Indonesia
FRENCH
They started French East India Company in 1664
In 1668 established 1st factory at Surat
They had factories at Machalipatnam, Chandernagore, Mahe, Karaikal, Balsore
The Governor General Dupleix had high ambitions to establish French as major power in South India
The high ambitions of Dupleix led to Carnatic wars with English
ENGLISH
Queen Elizabeth in 1600 issued a royal charter authorizing East India Company to trade with Eastern countries for 15 years
Mughal Emperor Jahangir issued a royal permission to English to Establish their 1st factory at Surat
They established factories at Agra, Ahmedabad, Braoch
In 1639 they established St George fort after taking Madras from King of Chandragiri
In 1690 on banks of Hoogly river they purchased 3 villages namely Sutanauti, Kalikata, Govindapur and built Fort william
By later part of 18th century they made Calcullat their capital city
CARNATIC WARS
The Portuguese and the Dutch got withdrawn from India unable to withstand the competition from French and English by 18th century, French and English resorted to show of strength in order to establish their political supremacy over India, the political instability had arised in the regions of Hyderabad and Carnatic, to take benefit of the situation French and English Fought 3 Carnatic wars
First Carnatic War

Consequences of War
A French Military leader La Bourdonnais from Mauritius invaded Madras and Captured it
The British requested the help of Anwaruddin, Nawab of Carnatic
The army sent by Nawab of Carnatic failed to defeat French at Madras
La Bourdonnais took money from English, returned Madras and went back to Mauritius
Dupleix tried to take Madras under control but failed, finally 1st carnatic war ended with treaty signed in Europe
Second Carnatic War

Consequences of War
French made Salabath Jung, another son of Asaf Jha as the Nizam of Hyderabad
In the Carnatic Chandasaheb became the Nawab with the help of French
Robert Clive of East India Company attacked Arcot, the capital city of Carnatic and defeated Chandasaheb
Chandasaheb was imprisoned and later killed in the war
In the Place of Chandasaheb, the English named Mohammed Ali the Son of Anwaruddin as the Nawab of Carnatic
French recalled Dupleix and suffered a political setback
Third Carnatic War

Consequences of War
Count de Lally of French attempted to beseige Wandiwash in 1760
Sir Eyre Coote of the English army defeated the French and imprisoned Bussy
Lally escaped and hide in Pondicherry
Sir Eyre Coote attacked Pondicherry and Lally was made to surrender unconditionally in 1761
The French lost all their bases and powers in India
English started consolidating their powers in India
As per the treaty singed Pondicherry was returned to French
BRITISH RULE IN INDIA
After obtaining political control over South India, the British tried to gain control over the rich Bengal province in the later part of 18th century, The East India Company was making considerable profits from this province. The Dastaks (Licence) issued by the Mughal ruler Faruk Siar were the main reasons for this,the Dastak was misused by them, and this led to confrontation between the Nawabs and the Company which paved way for two crucial wars : Battle of Plassey and Battle of Buxar.
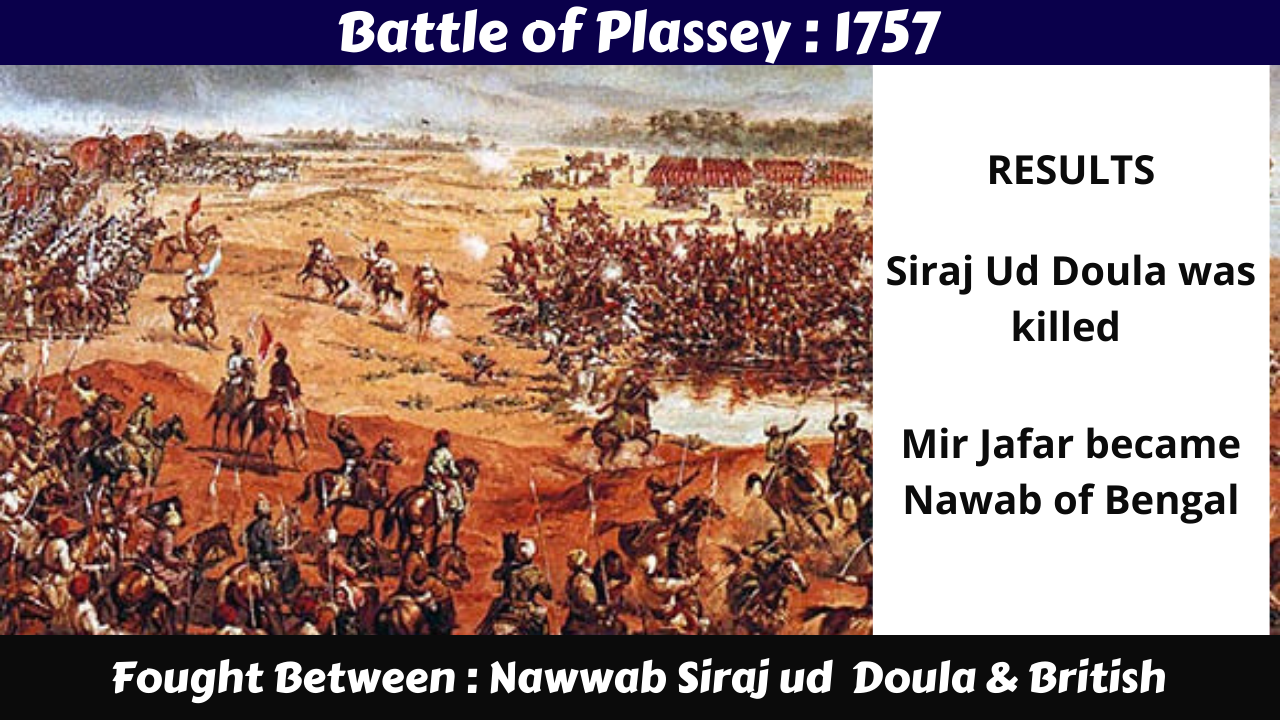
Battle of Plassey
Reasons
MISUSE OF DASTAK : Siraj Ud Doula was furious as Dastak (License) was misused by East India Company
MENDING OF FORT : Fort of Calcutta was mended by British and Canons were placed without permission
BLACK ROOM TRAGEDY : Siraj ud-Daulah conquered Fort William He imprisoned 146 Englishmen in a small room in the fort, of which 123 died
Consequences of War
Robert Clive got engraved with Black room tragedy and arrived in Bengal with a huge army.
Robert Clive attracted rich locals like Manikchand, Omichand, Jagath Seth and others towards him
Robert Clive Convinced Mir Jaffar, the military head of Siraj-ud-Daula to stay neutral in the battle by offering him the post of Nawab of Bengal
Outcomes
Siraj-ud-Daula who tried to escape from the battlefield, was captured and killed
Mir Jaffar became the Nawab of Bengal
The East India Company gained exclusive rights to trade in Bengal
As war indemnity for the attack of Fort William Mir Jaffar had to pay Rupees seventeen crores and seventy lakhs to Sirja-ud-Daulah
British projected Mir Jaffar as an inefficient Nawab and made in his nephew Mir Qasim the Nawab of Bengal
Battle of Buxar

Consequences of War
Mir Qasim declared himself an independent King
After verify misuse of Dastak by British he declared all business was duty free in Bengal
Indians started to compete with British in all Spheres of business and British trade got suffered
British to oppose the Nawab. They brought in Mir Jaffar again and dethroned Mir Qasim
Mir Qasim entered into agreements with the Mughal ruler Shah Alam-II and Nawab of Awadh ‘Shuja-ud-daula
Mir Qasim with his combined forces faced the British army led by Hector Munro at Buxar in 1764
Outcomes
Shah Alam-II accorded the Dewani rights over Bengal to the British
The rights over Bengal to the British were given back by Shah Alam-II for an annual fee of Rupees 26 lakhs
Rs 50 lakhs fine was imposed on the Nawab of Awadh for waging a war against the company
After the death of Mir Jaffar, the company took over the entire administration of Bengal and paid pension to his son










































